A stair is a sequence of steps provided to afford the means of ascent and decent between the floors or landing. The apartment or room of a building in which the stair is located is known as a staircase and the opening or space occupied by the stair is known as stairway.
Following are the common technical terms used in connection with the stairs-
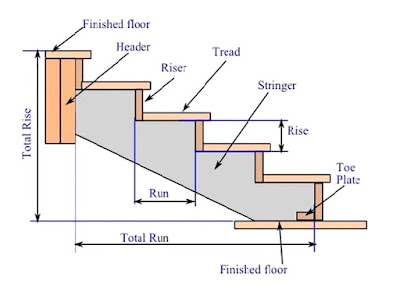
- Tread- The horizontal upper part of a step on which foot is placed in ascending or descending a stairway is called tread.
- Riser- A vertical portion of a step providing a support to the tread is called riser.
- Flier- A straight step having a parallel width of tread is called flier.
- Flight- An unbroken series of steps between two landing is called flight.
- Landing- A horizontal platform at the top or bottom of a flight between the floors is called landing. It facilitates change of direction and provides an opportunity for taking rest during the use of the stair.
- Rise- The vertical distance between two successive tread faces is called rise.
- Going- The horizontal distance between two successive riser face is called going.
- Nosing- The projecting part of the tread beyond the face of riser is called nosing.
- Scotia- A moulding provided under the nosing to beautify the elevation of a step and to provide strength to nosing is called scotia.
- Soffit- The under surface of a stair is called soffit.
- Pitch or slope- The angle which the line of nosing of the stair makes with the horizontal is called pitch or slope.
- Strings or stringers- The sloping members which support the steps in a stair are called strings or stringers.
- Baluster- The vertical member of wood or metal to support the hand rail is called baluster.
- Balustrade- The combined frame work of handrail and balusters is known as balustrade.
- Hand rail- The horizontal or inclined support provided at a convenient height is called hand rail.
- Newel post- The vertical member placed at the ends of flight connecting the ends of strings and hand rail is called newel post.
Notes:-
- The size of a step commonly adopted for residential building is 250 mm X 160 mm. In hospital etc. the comfortable size of step is 300 mm X 100 mm.
- The width of stairs depend upon its location in the building and the types of a building itself. In a residential building the average value of stair width is 900 mm while in a public building 1.5 to 1.8 metres width may be required.
- The width of landing should be greater than the width of stair.
- The pitch of stair should never exceed 40 degree.
- In designing a stair a comfortable slopes is achieved when the sum of going and twice the rise should be equal to 60 approximately.
- In designing a stair the product of going and the rise should be equal to 400.
- The clear distance between the tread and soffit of the flight immediately above it should not be less than 2 metres.
- An open newel stair consist of two or more straight flights arranged in such a manner that a clear space occurs between the background and forward flights.
- In wooden stairs the thickness of tread is adopted as 38 mm.